정렬
들어가기 전에
버블 정렬
버블 정렬은 브루트 포스 방법으로 배열의 요소를 모두 하나씩 비교하여 정렬하는 알고리즘이다. 배열 전체를 쭉 살펴보는 것을 n번 하기 때문에 시간 복잡도는 항상 $O(n^2)$ 이다. 가장 비효율적인 알고리즘이기 때문에 최대한 사용을 지양해야 한다.
병합 정렬
병합 정렬은 분할 정복 방법으로 배열의 모든 요소를 분해한뒤 정렬하여 다시 합치는 방법이다. 시간 복잡도는 $O(n logn)$ 이다. 병합 정렬의 작동 순서는 다음과 같다.
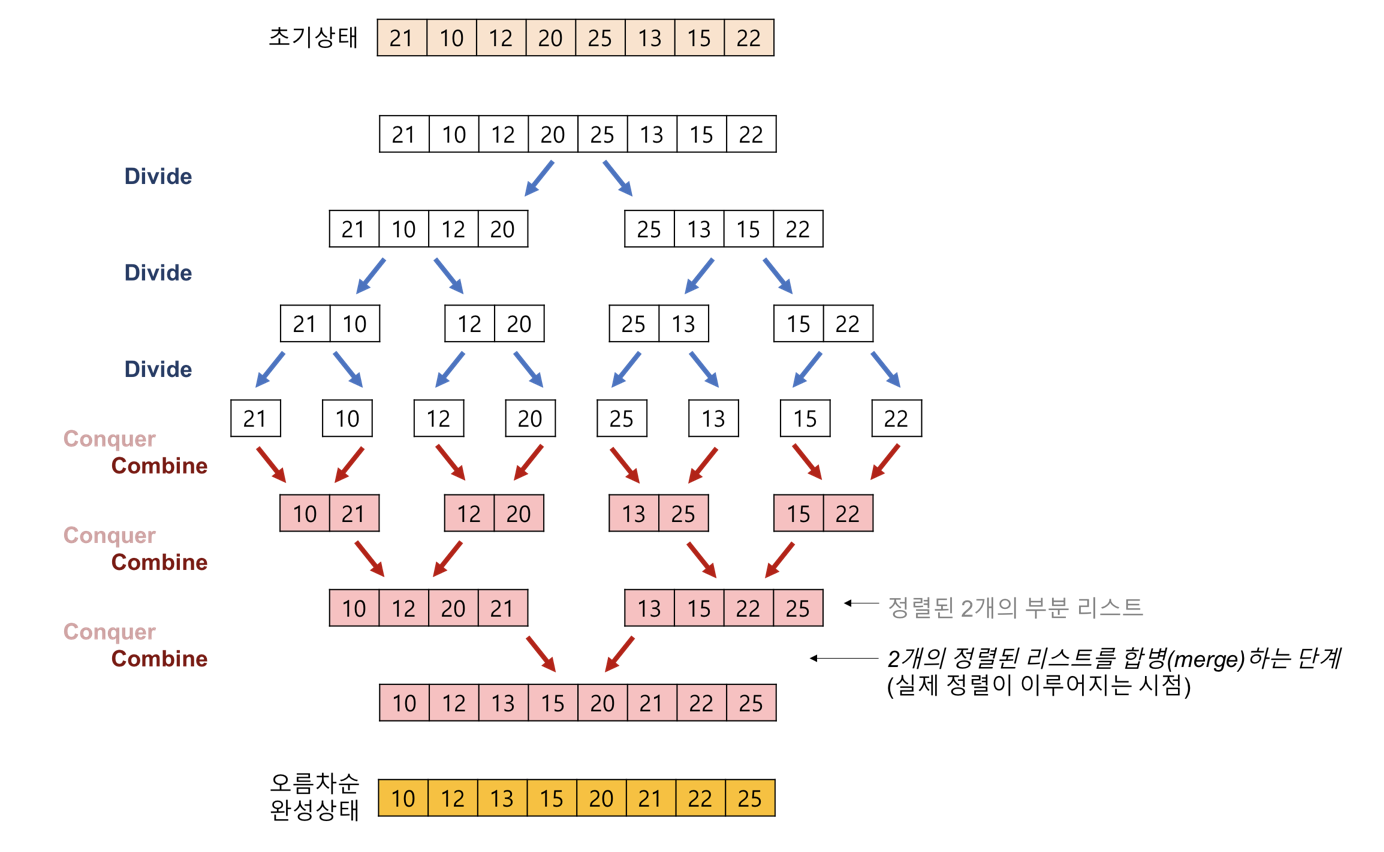
퀵 정렬
퀵 정렬은 병합 정렬과 마찬가지로 분할 정복 알고리즘이며 피봇이라는 개념이 추가되어 피봇보다 작으면 왼쪽, 크면 오른쪽과 같은 방식으로 파티셔닝 하면서 쪼개 나간다. 시간 복잡도는 $O(n logn)$ 이다. 이때, 이미 정렬된 배열에 퀵 정렬을 적용하면 n번에 걸쳐 전체를 비교하기 때문에 버블 정렬과 다를 바 없는 최악의 성능을 보여준다. 퀵 정렬의 작동 순서는 다음과 같다.
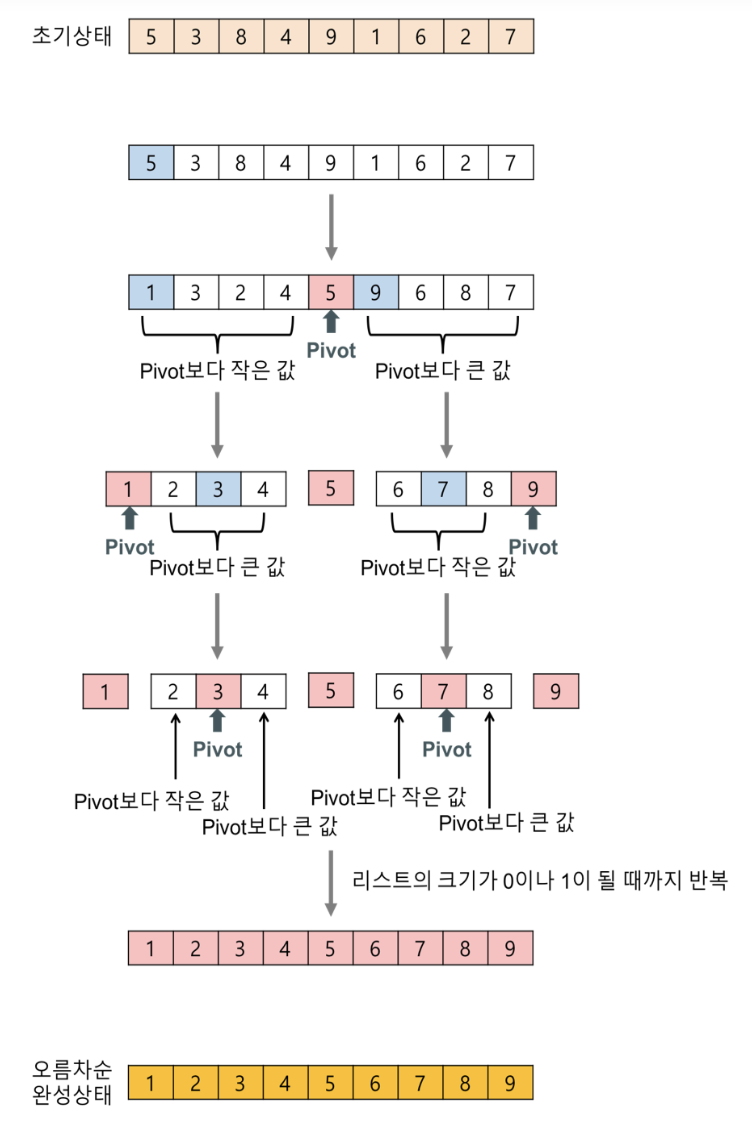
Question 58: 리스트 정렬
연결 리스트를 $O(n logn)$ 에 정렬하라.
입력: 4->2->1->3
출력: 1->2->3->4
풀이 1: 병합 정렬
class Solution:
# 두 정렬 리스트 병합
def mergeTwoLists(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if l1 and l2:
if l1.val > l2.val:
l1, l2 = l2, l1
l1.next = self.mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2)
return l1 or l2
def sortList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if not (head and head.next):
return head
# 런너 기법 활용
half, slow, fast = None, head, head
while fast and fast.next:
half, slow, fast = slow, slow.next, fast.next.next
half.next = None
# 분할 재귀 호출
l1 = self.sortList(head)
l2 = self.sortList(slow)
return self.mergeTwoLists(l1, l2)
중요 내용
- sortList는 배열의 요소를 단일 아이템으로 쪼개는 함수이다.
- mergeTwoLists는 배열의 요소를 정렬하면서 이어 붙이는 함수이다.
풀이 2: 퀵 정렬
파이썬을 이용하여 퀵 정렬을 할시 타임아웃이 떠서 풀지 못한다.
풀이 3: 내장 함수를 이용하는 실용적인 방법
# Definition for singly-linked list.
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.next = None
class Solution:
def sortList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
# 연결 리스트 -> 파이썬 리스트
p = head
lst: List = []
while p:
lst.append(p.val)
p = p.next
# 정렬
lst.sort()
# 파이썬 리스트 -> 연결 리스트
p = head
for i in range(len(lst)):
p.val = lst[i]
p = p.next
return head
중요 내용
- 연결 리스트를 일반 리스트로 변경 후에 정렬한 뒤에 다시 연결 리스트로 변경하는 방법이다.
- 제일 직관적이면서 쉬운 방법이다.
Question 59: 구간 병합
겹치는 구간을 병합하라.
입력: [[1,3],[2,6],[8,10],[15,18]]
출력: [[1,6],[8,10],[15,18]]
풀이 1: 정렬하여 병합
class Solution:
def merge(self, intervals: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
merged = []
for i in sorted(intervals, key = lambda x:x[0]):
if merged and i[0] <= merged[-1][1]:
merged[-1][1] = max(merged[-1][1], i[1])
else:
merged += i,
return merged
중요 내용
- merged 변수의 마지막 요소의 두번째 값(최댓값)과 입력값의 첫번째 값(최솟값)을 비교해가며 서로 겹치는지 확인한다.
- 콤마(,) 연산자는 중첩 리스트로 만들어주는 연산을 한다.
Question 60: 삽입 정렬 리스트(재풀이)
연결 리스트를 삽입 정렬로 정렬하라.
입력: [4,2,1,3]
출력: [1,2,3,4]
풀이 1: 삽입 정렬
class Solution:
def insertionSortList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
cur = parent = ListNode(None)
while head:
while cur.next and cur.next.val < head.val:
cur = cur.next
cur.next, head.next, head = head, cur.next, head.next
cur = parent
return cur.next
중요 내용
- head는 정렬을 할 대상이며, cur은 정렬을 끝낸 대상이다.
- 정렬을 끝낸 cur은 이미 정렬된 상태이므로, 정렬을 해야 할 대상 head와 비교하면서 더 작다면 계속 cur.next를 이용해 다음으로 이동한다.
- 찾은 cur 위치 다음에 head가 들어가고, head.next에는 cur.next를 연결해 계속 이어지게 한다. 그리고 head는 head.next 차례를 이어받는다.
- 마지막으로 cur=parent를 통해 다시 처음으로 되돌아가 처음부터 비교한다.
- 정렬이 이루어지는 순서를 다음과 같이 정리해보았다.
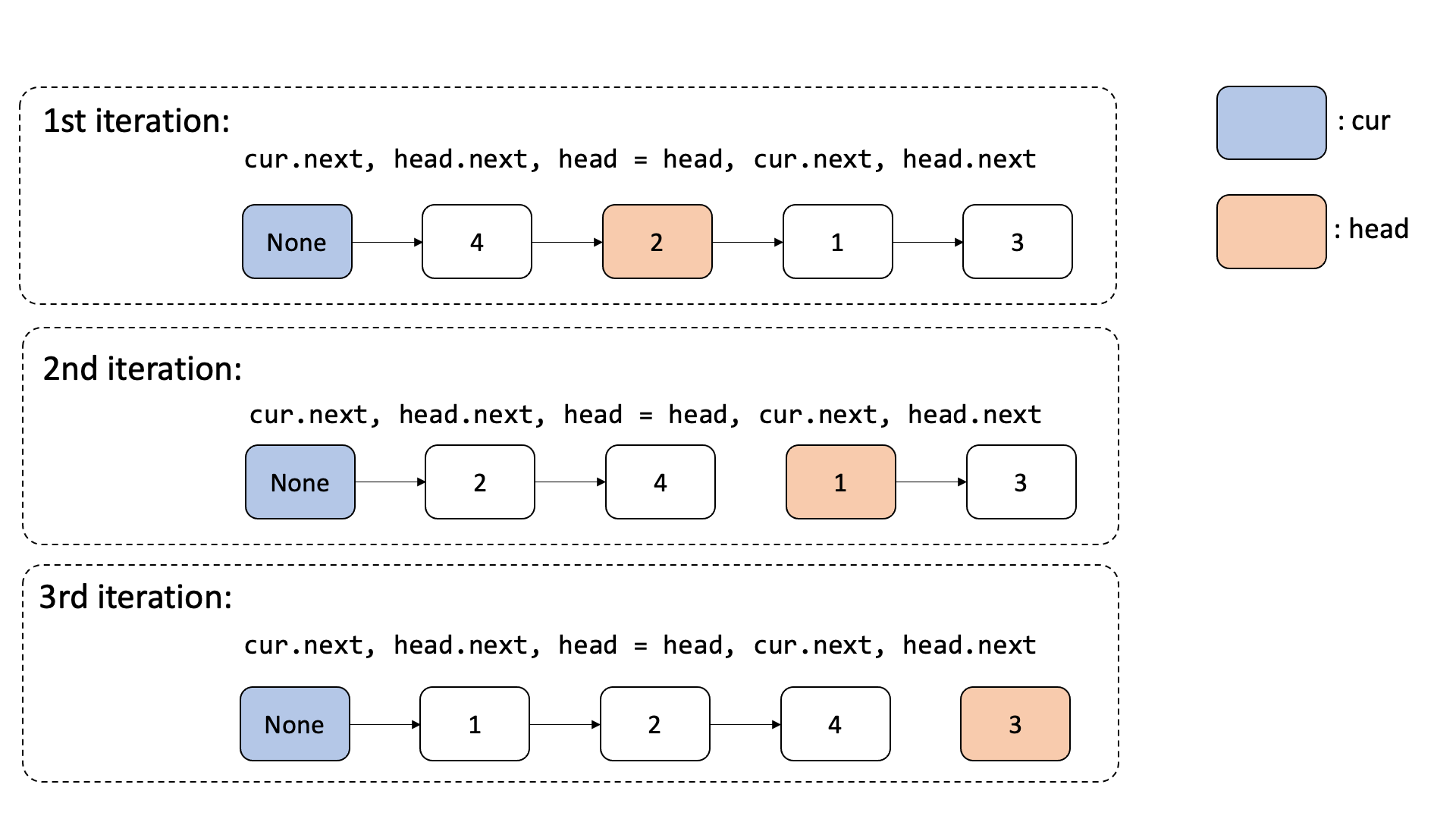
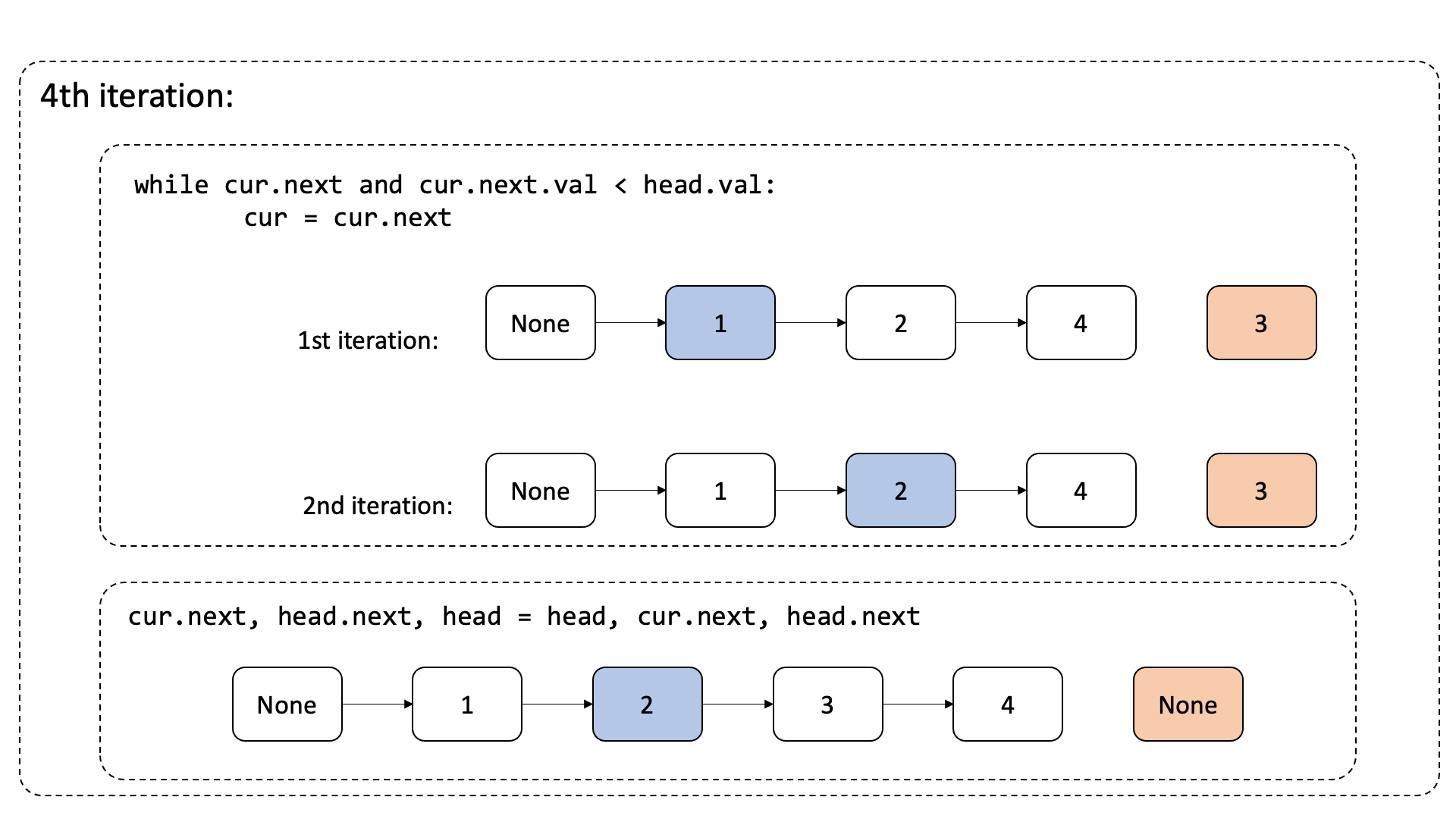
풀이 2: 삽입 정렬의 비교 조건 개선
class Solution:
def insertionSortList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
cur = parent = ListNode(0)
while head:
while cur.next and cur.next.val < head.val:
cur = cur.next
cur.next, head.next, head = head, cur.next, head.next
if head and cur.val > head.val:
cur = parent
return parent.next
중요 내용
- 다음번 head가 cur보다 큰 상태라면 굳이 되돌아가지 않아도 된다. 따라서 불필요한 과정을 생략하기 위해 cur=parent 앞에 cur값이 head보다 큰 경우에만 돌아가도록 조건문을 추가하였다.
- 해당 조건문 하나로 기존 대비 10배 이상의 성능을 높일 수 있었다.
Question 61: 가장 큰 수(재풀이)
항목들을 조합하여 만들 수 있는 가장 큰 수를 구하라.
입력: nums = [3,30,34,5,9]
출력: “9534330”
풀이 1: 삽입 정렬
class Solution:
def to_swap(self, n1:int, n2:int) -> bool:
return str(n1) + str(n2) < str(n2) + str(n1)
def largestNumber(self, nums: List[int]) -> str:
i = 1
while i < len(nums):
j = i
while j > 0 and self.to_swap(nums[j-1], nums[j]):
nums[j], nums[j-1] = nums[j-1], nums[j]
j -= 1
i += 1
return str(int(''.join(map(str, nums))))
중요 내용
- to_swap은 숫자를 반대로 조합했을 때 더 큰지 여부를 체크하는 함수이다.
- 만약 더 크다면 해당 숫자가 배열의 그 전의 인덱스의 값보다 앞에 위치하게 된다.
- 1,2 과정은 while 문을 통해 반복하게 한다.
Question 62: 유효한 애너그램
t가 s의 애너그램인지 판별하라.
입력: s = “anagram”, t = “nagaram”
출력: True
내 풀이
class Solution:
def isAnagram(self, s: str, t: str) -> bool:
return sorted(s) == sorted(t)
- 매우 간단하게 풀었다.
결과
Runtime: 91 ms, faster than 22.28% of Python3 online submissions for Valid Anagram. Memory Usage: 15 MB, less than 20.23% of Python3 online submissions for Valid Anagram.
풀이 1: 정렬을 이용한 비교
내 풀이 방법과 동일하기 때문에 설명을 생략하겠다.
Question 63: 색 정렬
빨간색을 0, 흰색을 1, 파란색을 2라고 할 때 순서대로 인접하는 제자리 정렬을 수행하라
입력: nums = [2,0,2,1,1,0]
출력: [0,0,1,1,2,2]
풀이 1: 피벗을 이용한 풀이
class Solution:
def sortColors(self, nums: List[int]) -> None:
red, white, blue = 0, 0, len(nums)
while white < blue:
if nums[white] < 1:
nums[red], nums[white] = nums[white], nums[red]
white += 1
red += 1
elif nums[white] > 1:
blue -= 1
nums[white], nums[blue] = nums[blue], nums[white]
else:
white += 1
중요 내용
- i,k 를 양쪽 포인터로 두고 j가 이동하면서 중간값을 기준으로 스왑하는 형태로 구현되어 있다.
- 1보다 작으면 왼쪽, 1이면 중간, 1보다 크면 오른쪽에 위치하도록 한다.
Question 64: 원점에 k번째로 가까운 점
평면상에 points 목록이 있을 때, 원점 (0,0) 에서 k번쨰로 가까운 점 목록을 순서대로 출력하라. 평면상 두 점의 거리는 유클리드 거리로 한다.
입력: points = [[1,3],[-2,2]], k = 1
출력: [[-2,2]]
내 풀이
class Solution:
def kClosest(self, points: List[List[int]], k: int) -> List[List[int]]:
for x in points:
x.append(x[0]**2+x[1]**2)
points.sort(key=lambda x:x[2])
for x in points:
x.pop()
return points[:k]
결과
Runtime: 912 ms, faster than 73.96% of Python3 online submissions for K Closest Points to Origin. Memory Usage: 20.4 MB, less than 56.62% of Python3 online submissions for K Closest Points to Origin.
풀이 1: 유클리드 거리의 우선순위 큐 순서
class Solution:
def kClosest(self, points: List[List[int]], K: int) -> List[List[int]]:
heap = []
for (x, y) in points:
dist = x ** 2 + y ** 2
heapq.heappush(heap, (dist, x, y))
result = []
for _ in range(K):
(dist, x, y) = heapq.heappop(heap)
result.append((x, y))
return result
중요 내용
- 내가 사용했던 풀이 방법과 비슷하나 여기서는 heapq 모듈을 사용하여 최솟값부터 차례로 출력하게 하였다.

Comments