Inception-v4, Inception-ResNet and the Impact of Residual Connections on Learning
Abstract
- Inception and residual network have yielded outbreaking performace in the 2015 ILSVRC challenge.
- This paper proves that applying residual connection to inception networks accelerates the training process significantly.
Introduction
- Since inception network tend to get very deep, replacing filter concatenation stage of the Inception architecture with residual architecture is very effective.
- In this paper, they compared two pure Inception variants, Inception-v3 and v4, to two other variants with similarly expensive Inception-ResNet variants.
Architectural Choices
1. Pure Inception blocks
General look
Large scale of Inception-v4 looks as follows:
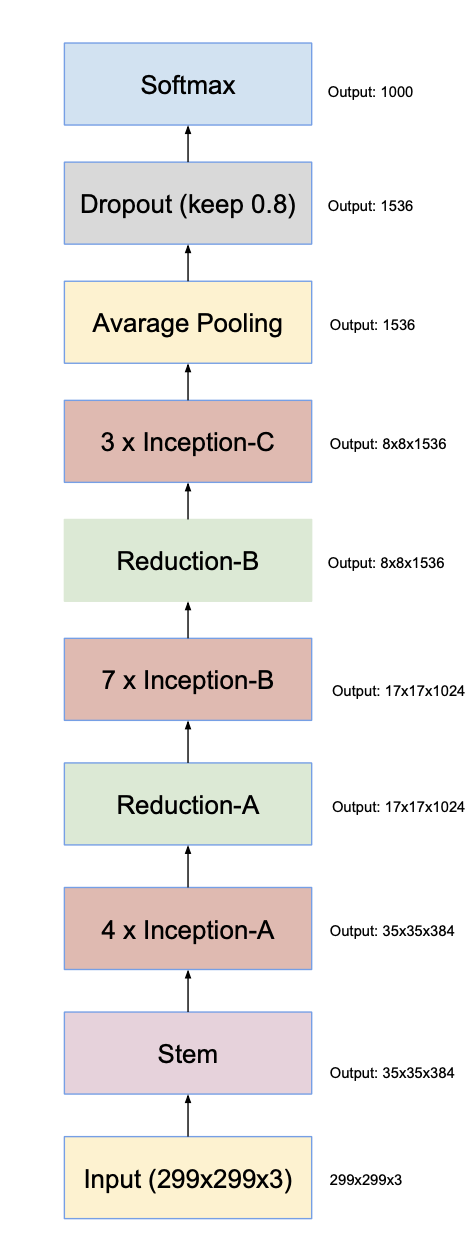
- Previous inception networks tend to be very conservative about changing the architectural choices, and had various forms among structures.
- Inception-v4 tackled the problems that previous inception networks had by making uniform choices for the inception blocks.
Stem
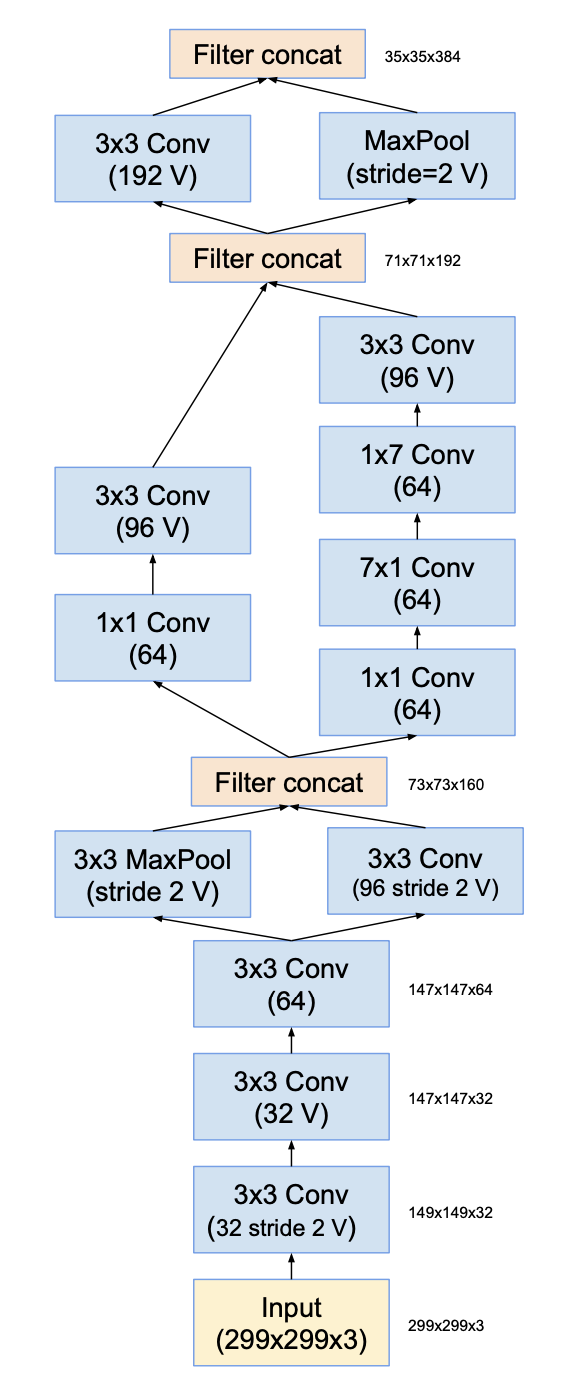
- ‘V’ in the figures indicates valid padding, which input grid size and output grid size differ.
- figures not marked with ‘V’ indicates same padding, which input grid size matches output grid size.
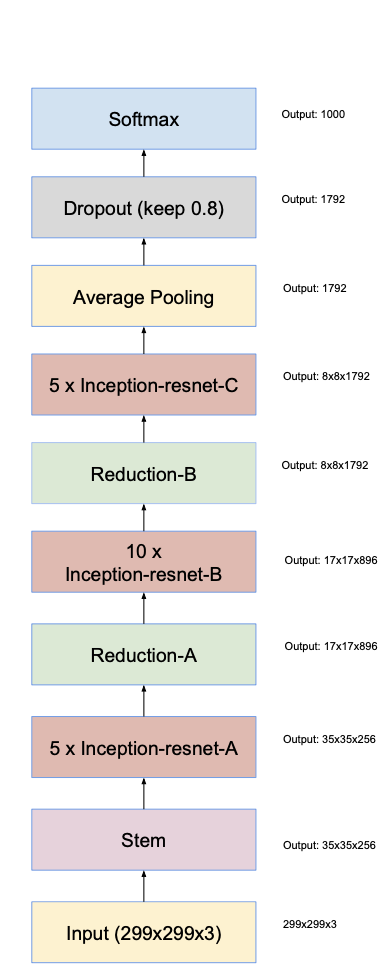
- Stem structure is used for input part of Inception-v4 and Inception-ResNet-v2 networks.
- Input size is 299x299x3, and output size is 35x35x384
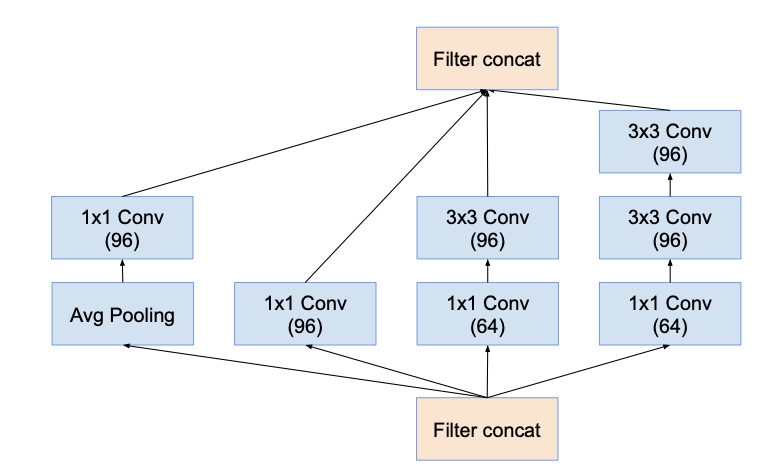
Inception-A
Inception-B
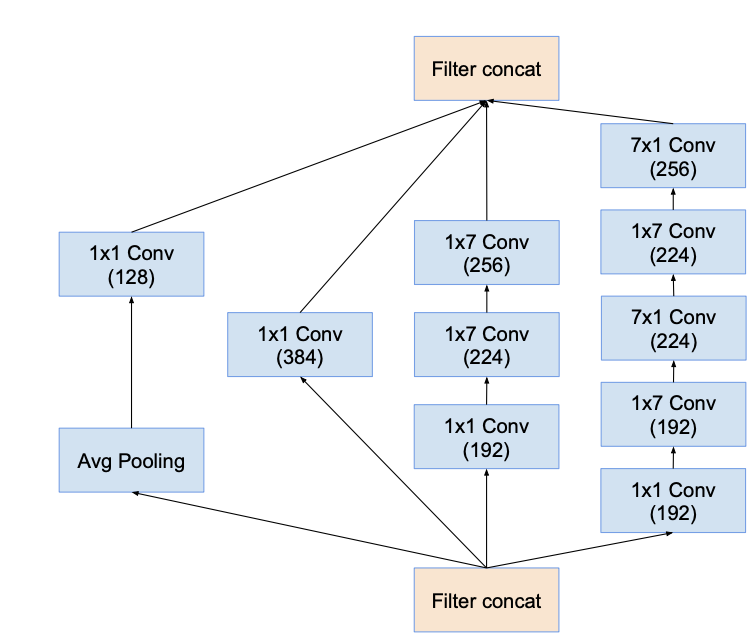
Inception-C
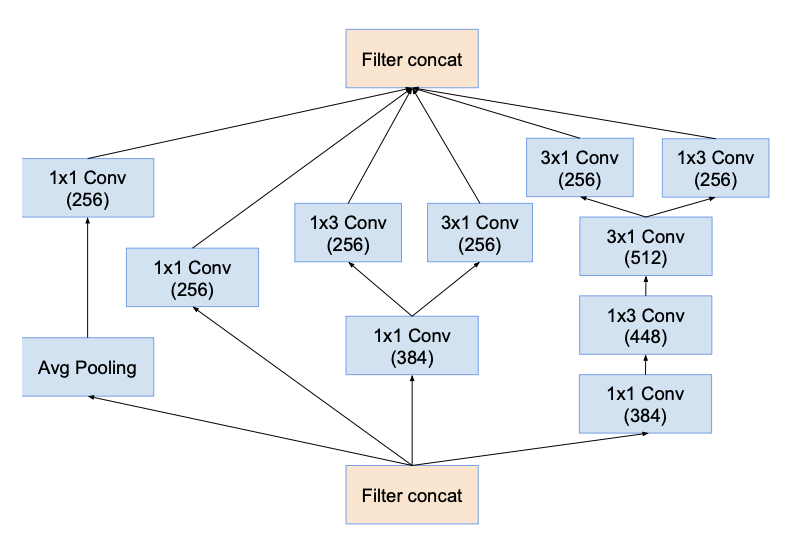
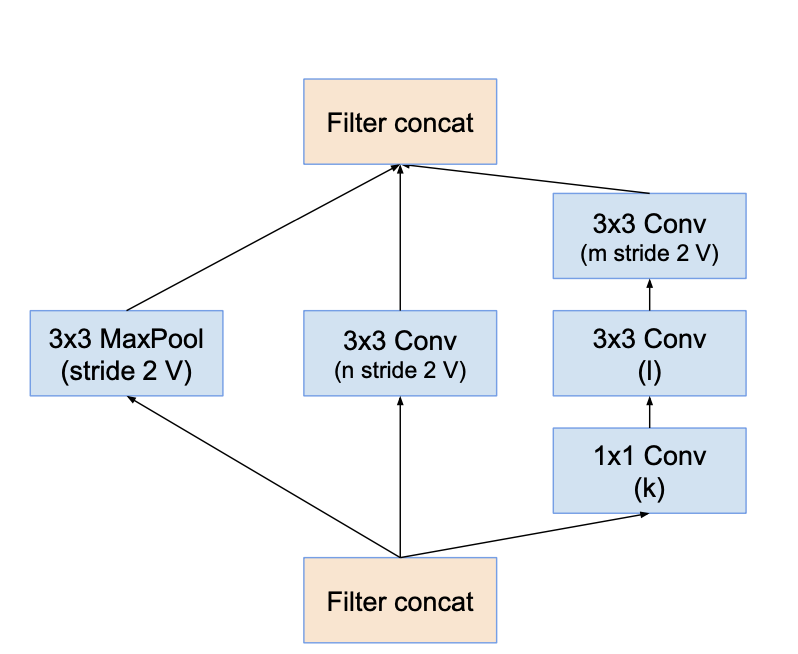
- k, l, m, n indicated varying filter sizes
Reduction-A
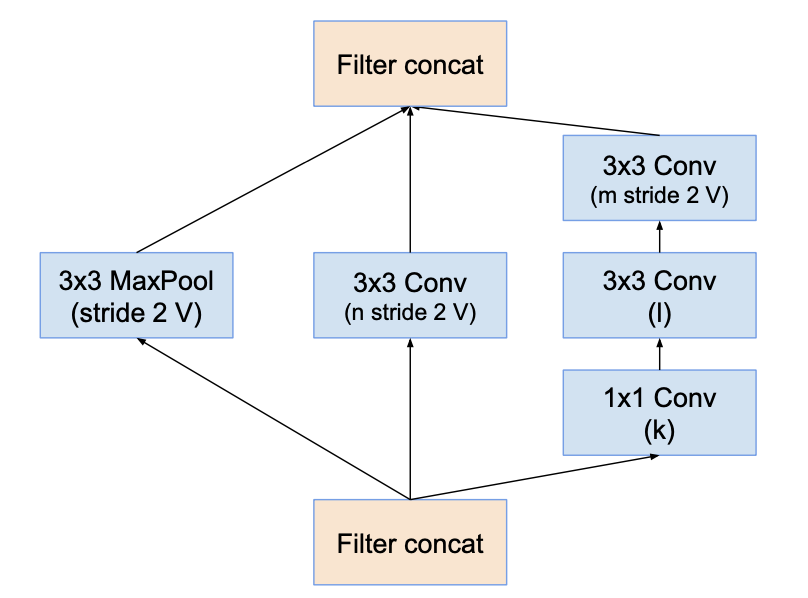
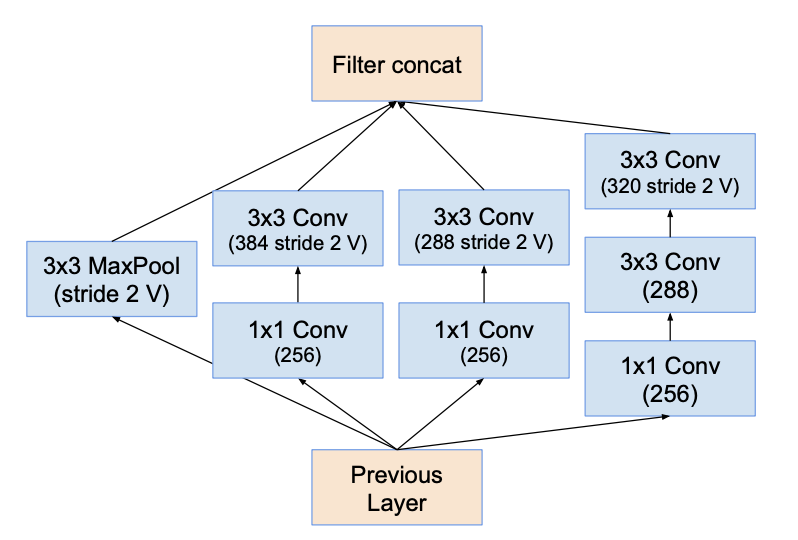
Reduction-B
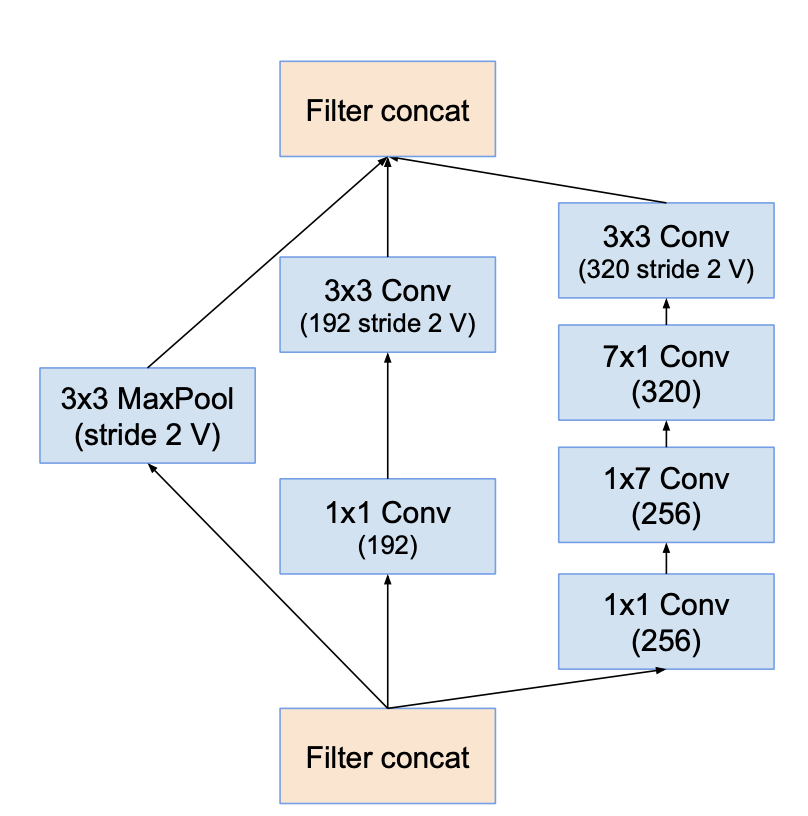
2. Residual Inception Blocks
Inception-ResNet-v1 and Inception-ResNet-v2 networks looks as follows:
-
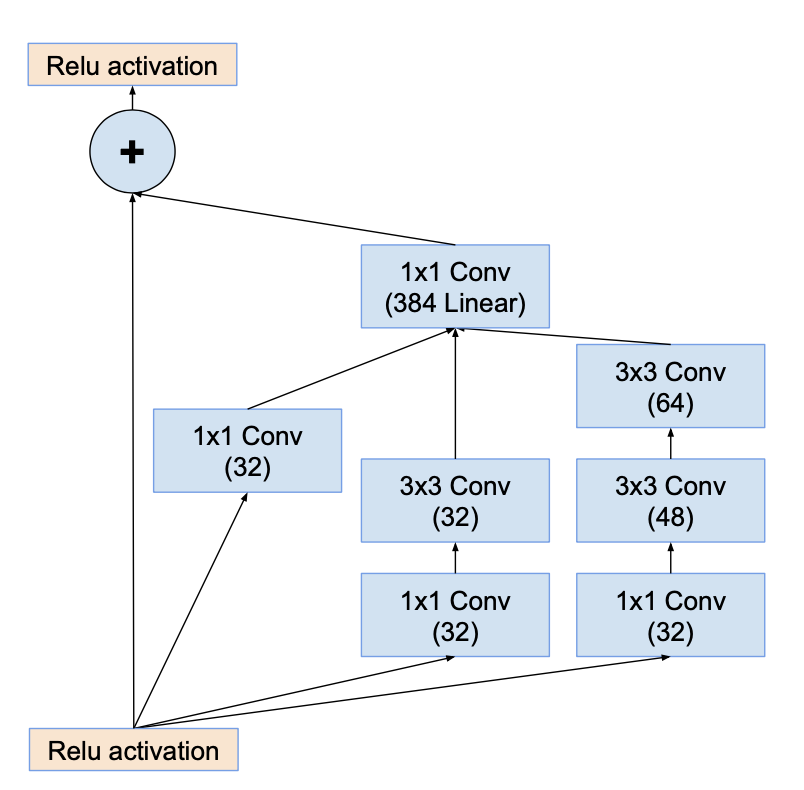
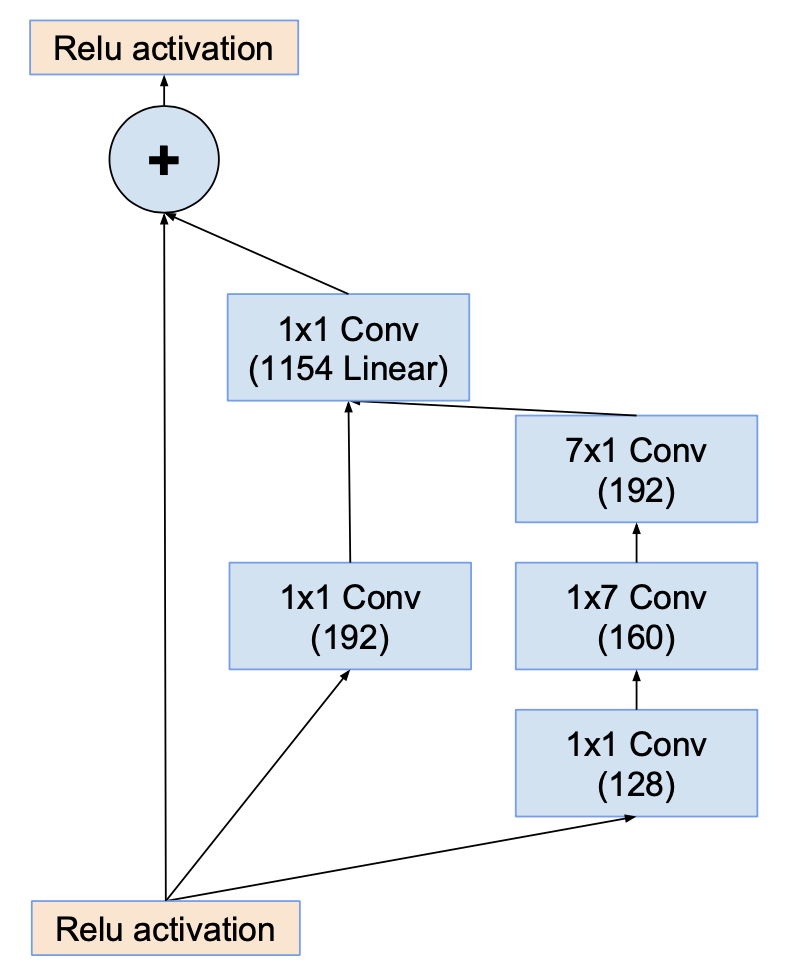
Each Inception block starts with 1x1 convolution layer, which is used for scaling up the dimensionality of the filter banks. This later compensates to dimensionality reduction caused by inception block.
-
Batch normalization is applied only on traditional layers, not on top on summations. This has significantly less GPU memory usage compared to model with BN applied to all layers.
Inception-resnet-A
Reduction-A
Inception-resnet-B
Reduction-B
Inception-resnet-C
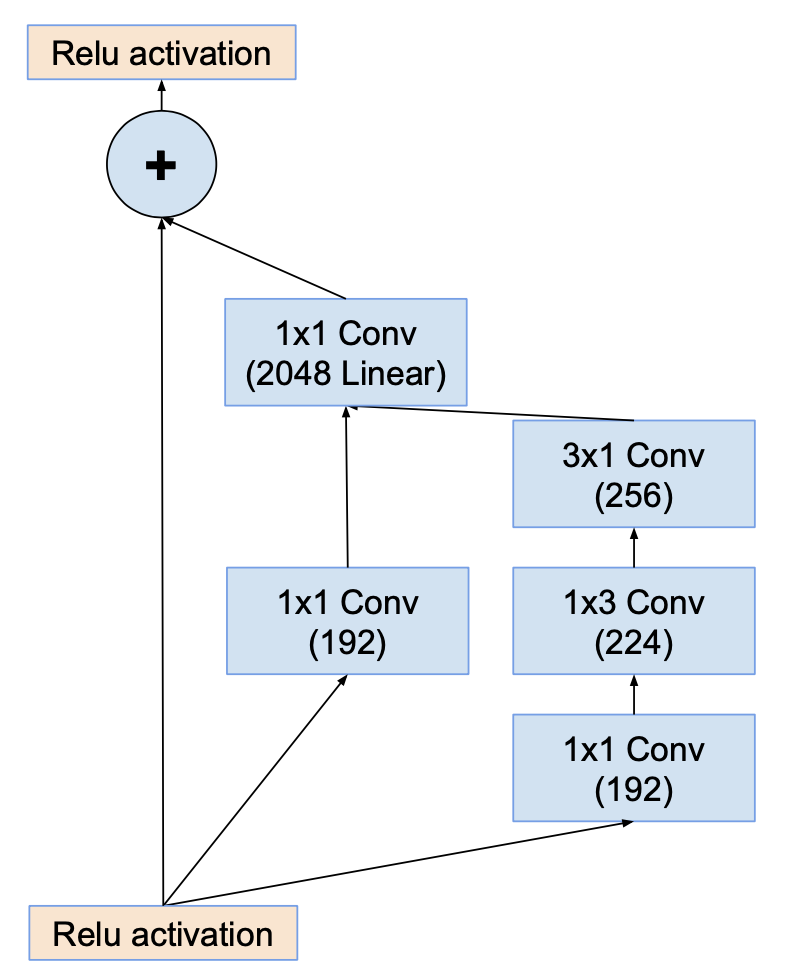
Scaling of the residuals
- If number of filters exceed 1000, networks die, meaning last layer before average pooling starts to produce only zeros.
- This problem is solved by scaling down residuals before being added to the accumulated layer activations.
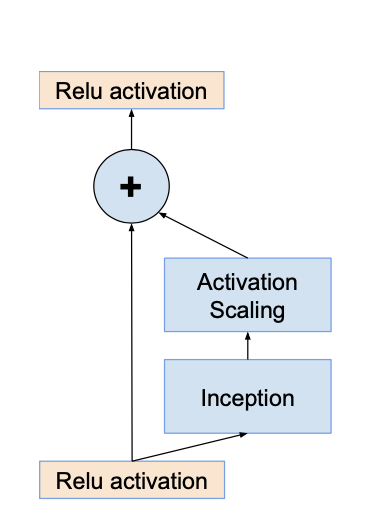
Training Methodology
- Best models were achieved using RMSProp with a learning rate of 0.045.
Experimental Results
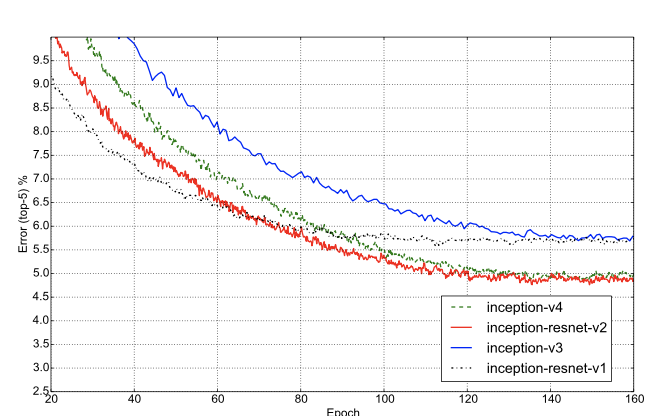
- The graph below shows the top-5 error evaluations of all four models. Inception with residual block converges much faster than pure Inception networks, while having similar performance.
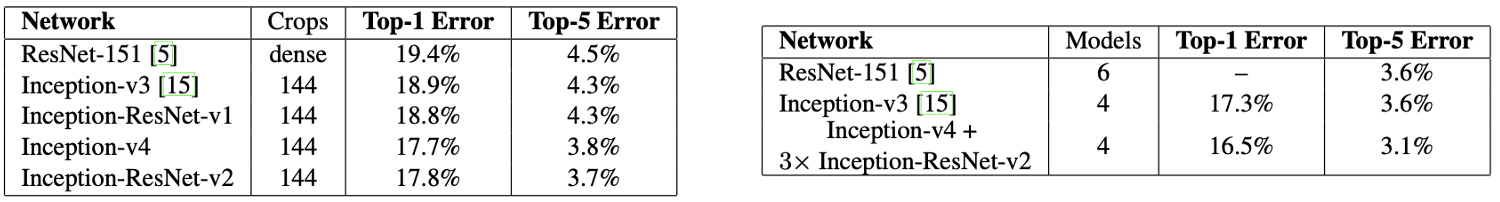
- Test on 144 crop images were also conducted. Ensembled Model, which consists of one pure Inception-v4 model and three Inception-ResNet-v2 models, was used for evalution. Table on the left refers to the error rate of single model while the right refers to error rate of ensembled model. Ensembled model showed slightly better performance than single model.
Conclusions
- Inception networks with residual connections, inception-resnet-v2, showed fastest training speed, while having similar performance with pure counterparts.
- Residual connections contribute heavily to improving training speed of inception networks.

Comments