Information Extraction
Background
In traditional information extraction using LLMs, few-shot examples were constructed through lexical (e.g., BM25) or semantic (e.g., cosine similarity) based retrieval.
Problem Definition
Existing retrieval methods tended to prioritize fetching documents that contained the answer to the query. Therefore, if the retrieval corpus did not contain the answer to the query, the performance of information extraction dropped sharply.
Solution
We proposed performing syntax-based retrieval instead of semantic-based. Documents are represented as a tree structure based on their grammar, and the similarity is calculated using the tree edit distance. Documents with high similarity are then fetched to construct the few-shot examples.
Achievements
- Achieved a performance improvement of about 2% compared to existing methods.
- We created a metric to evaluate the extent to which retrieved documents contain the answer to the query. This evaluation confirmed that our proposed method achieves the highest information extraction performance while including the least amount of direct answers in the retrieved documents.
- Accepted to ACL 2025 Findings.
My Role
- As the first author, I was responsible for the planning, experimentation, and writing of the research paper.
- Fine-tuned RoBERTa and BART for baseline implementation.
- Implemented syntax-based retrieval using LlamaIndex.
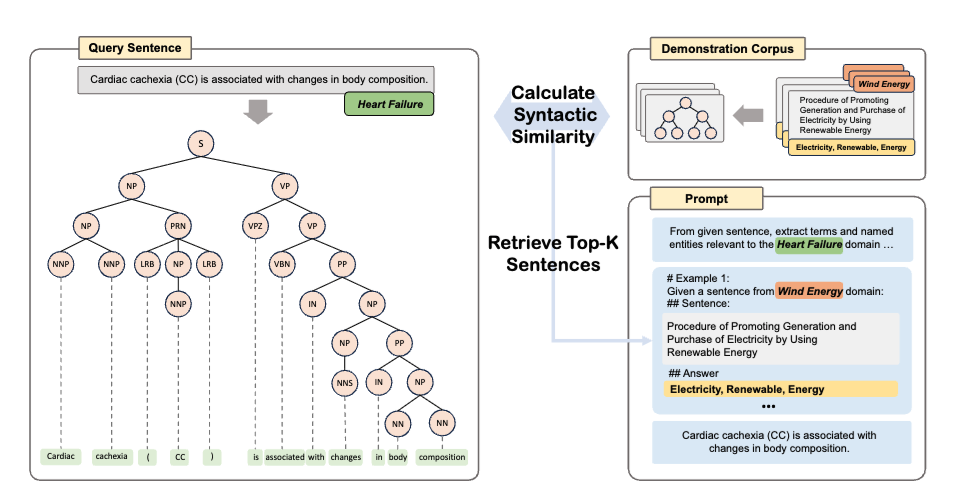
Method overview.